
Sep . 28, 2024 02:32 Back to list
Sodium Nitrite Safety Data Sheet from Manufacturer for Proper Handling and Use
Understanding Sodium Nitrite Safety and Usage Guidelines
Sodium nitrite, a chemical compound with the formula NaNO2, is widely used in various industries, particularly in food preservation, pharmaceuticals, and chemical manufacturing. Due to its numerous applications, understanding its properties, safety protocols, and the guidelines set forth by manufacturers is essential for safe handling.
Properties of Sodium Nitrite
Sodium nitrite is a white or yellowish crystalline powder, highly soluble in water, which enables its effective use in different solutions. It serves as a preservative and an antioxidant in processed meats, helping to prevent bacterial growth and preserve color. Additionally, sodium nitrite is utilized in dye manufacturing, rubber processing, and as a corrosion inhibitor in cooling systems.
Safety Data and MSDS
The Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) provided by manufacturers outlines essential safety information regarding sodium nitrite. Users must familiarize themselves with this document to ensure safe handling and emergency response procedures are understood. The MSDS includes critical data such as physical and chemical properties, health hazards, first-aid measures, handling and storage recommendations, and disposal considerations.
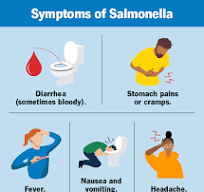
Health Hazards Sodium nitrite poses several health risks if mismanaged. It can cause irritation to the skin, eyes, and respiratory tract. Ingestion of sodium nitrite can lead to more severe health effects, including nausea, vomiting, and even methaemoglobinaemia, a condition where hemoglobin is modified, reducing the blood's ability to carry oxygen.
sodium nitrite msds manufacturer
Handling and Storage
When working with sodium nitrite, it is vital to wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves, goggles, and respiratory protection, especially in environments with inadequate ventilation. The chemical should be stored in a cool, dry place away from incompatible substances, including strong acids and oxidizing agents. Containers should be clearly labeled, and areas where sodium nitrite is stored should be secure to prevent accidental exposure.
Emergency Measures
In the event of accidental exposure or spills, the MSDS outlines a series of steps to mitigate risks. For skin contact, it is advised to wash the affected area thoroughly with soap and water. In case of inhalation or ingestion, immediate medical attention is necessary. The MSDS provides emergency contact numbers for poison control and other relevant resources.
Conclusion
In conclusion, sodium nitrite is an essential chemical used across various sectors. However, it is imperative to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and MSDS recommendations to ensure safe usage. By understanding the properties and risks associated with sodium nitrite, users can effectively prevent accidents and promote safety in the workplace. Always consult the latest regulatory materials and best practices to stay informed about the proper handling of sodium nitrite and its applications.
-
Premium China Bacillus Subtilis Supplier & Factory Solutions
NewsJul.30,2025
-
Premium Avermectin Supplier in China | Custom Solutions Available
NewsJul.29,2025
-
China Bacillus Subtilis Supplier - Custom Factory Solutions
NewsJul.29,2025
-
China Salivation: Leading Custom Salivation Supplier & Factory Solutions
NewsJul.29,2025
-
Leading Lincomycin Hydrochloride Manufacturer & Supplier with High Purity
NewsJul.29,2025
-
Bio-Enzyme Yogurt Growth Promoter Factory - Top Quality Manufacturer & Supplier
NewsJul.28,2025




