
Nov . 30, 2024 07:39 Back to list
china chickens and salmonella
Chickens and Salmonella in China A Growing Concern
In recent years, food safety has emerged as a pressing issue in China, particularly concerning poultry products. Among various pathogens, Salmonella has become a significant public health concern linked to chicken consumption. With the increasing demand for chicken meat in the country, understanding the relationship between Chinese poultry farming practices and the prevalence of Salmonella is vital.
Chickens and Salmonella in China A Growing Concern
The prevalence of Salmonella in chickens can often be attributed to farming practices, biosecurity measures, and overall hygiene standards within poultry farms. Many small-scale farms may lack the resources to implement rigorous biosecurity protocols, making them more susceptible to outbreaks of bacterial infections. This situation is exacerbated by the overcrowding of birds in some facilities, which creates an environment conducive to the spread of pathogens like Salmonella.
china chickens and salmonella
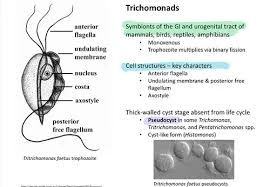
To combat the issue of Salmonella, the Chinese government has initiated various measures aimed at improving food safety standards. Strict regulations and inspections of poultry farms have been enforced to ensure compliance with hygiene practices. Furthermore, there has been an emphasis on educating farmers about the importance of biosecurity and safe handling practices to minimize contamination risks.
Consumer awareness also plays a crucial role in tackling Salmonella-related illnesses. Public health campaigns have focused on promoting safe cooking methods, such as thorough cooking of chicken to an internal temperature that effectively kills harmful bacteria. Additionally, consumers are urged to practice good hygiene in their kitchens, including washing hands and surfaces often to prevent cross-contamination.
Despite these efforts, challenges remain. The scale of poultry production in China continues to grow, and ensuring consistent compliance with safety regulations across numerous farms can be daunting. Continuous monitoring and research into best practices for disease control are necessary to reduce the incidence of Salmonella in chickens effectively.
In conclusion, while the chicken industry in China presents a significant source of protein for millions, it is crucial to address the potential health risks posed by Salmonella. By enhancing farming practices, strengthening regulatory frameworks, and promoting consumer education, China can strive towards a safer poultry supply chain. Increased vigilance and ongoing efforts are essential to minimize the risk of Salmonella and protect public health.
-
China Salivation AI with GPT-4 Turbo Features
NewsAug.01,2025
-
Epic Sepsis Factories: AI-Driven Detection with GPT-4 Turbo
NewsJul.31,2025
-
Acute Salpingitis and Oophoritis AI Factory
NewsJul.31,2025
-
Premium China Bacillus Subtilis Supplier & Factory Solutions
NewsJul.30,2025
-
Premium Avermectin Supplier in China | Custom Solutions Available
NewsJul.29,2025
-
China Bacillus Subtilis Supplier - Custom Factory Solutions
NewsJul.29,2025




